
Most Common Nutrient Deficiencies in Older Adults
Intake of necessary nutrition is essential for individuals of all ages but it becomes critical as an individual reaches old age. Good nutrition crucially impacts all aspects of life, including physical, mental, and social health. As men and women age, their activity levels decrease, leading to a decrease in appetite. This low caloric intake often becomes one of the key factors in creating deficient levels of vitamins and minerals. The dietary deficiencies are also compounded by the presence of age-related chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Why Do Seniors Lose Their Appetite?
Sudden loss of appetite and diminishing weight are not normal for anyone, irrespective of age. Why seniors experience such symptoms requires immediate medical evaluation to ascertain the reason. Loss of appetite can occur due to the following:
- Depression
- Stomach ulcers
- Cancers
- Dysphagia
- Thyroid issues
- Poor-fit dentures
- Failing sense of taste and smell
Work with your loved one's doctor instead of turning to a supplement immediately, and see if the underlying issues improve.
What are the main causes of nutrient deficiencies in seniors?
There are many causes that lead to dietary nutrient deficiency in older adults all over the world with degree of deficiencies varying from person to person. Some key causes of deficiencies are:
- Poor nutrient and dietary intake in the form of daily food consumption
- Physiological changes experienced by aging adults like forgetfulness, and loss of appetite
- Limiting financial conditions that impact quality food purchasing decisions
- Taking medications that hinder the body’s ability to absorb nutrients
As older adults are faced with physical, physiological and cognitive changes, poor dietary habits can result in the progression of chronic diseases like type II diabetes, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and malnutrition. The lack of required nutrition in the body can lead to a decline in the general quality of life that relates to decreased physical function and cognitive decline. Other physical loss includes a decrease in bone density that increases the risk of osteoporosis. Loss of muscle mass, and malnutrition are issues related to older age which result in loss of strength, endurance and resistance to diseases.
Thus, the adoption of nutrient-rich foods can be a measure to tackle the situation of nutritional deficiencies and promote a healthy lifestyle.
The table below shares some common signs of nutritional deficiencies
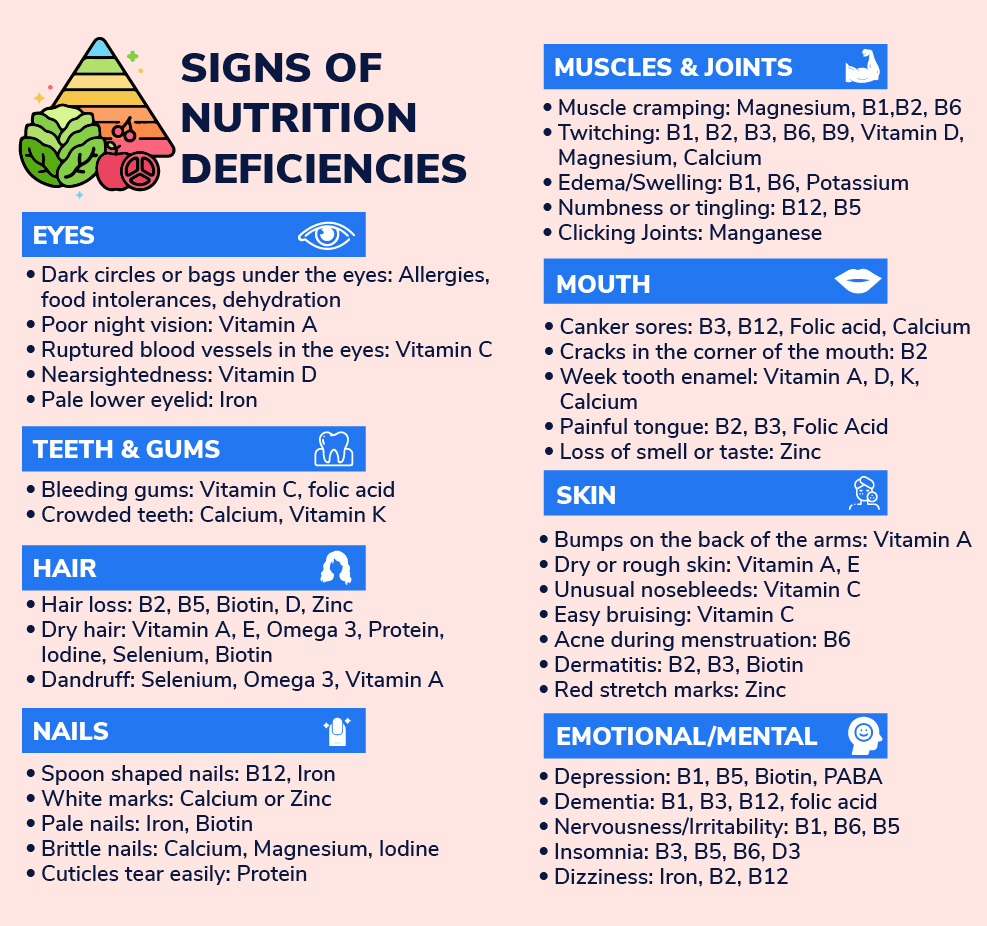
Nutritional Deficiencies in Senior Adults
Aging brings on lesser physical activity and caloric intake. Nutrition deficiency becomes common as fewer essential minerals and vitamins get absorbed. The prevalence of nutritional deficiencies in seniors also occurs due to the following:
- Cognitive impairments like forgetfulness
- A reduced or limited income which limits the amount spent on food
- Side-effects of prolonged medication
- Interaction of certain medications with some vitamins and minerals
- Gastrointestinal issues and major surgical procedures.
- Smoking, tobacco usage, and over-consumption of alcohol.
- Neurotransmitter and hormonal changes.
How important are vitamins and minerals for maintaining good health?
As people enter their sixties and seventies, they are bound to feel weak due to nutritional deficiencies. Some of the most common deficiencies that seniors may have are:
Calcium
Leafy greens like kale and spinach, dairy products, and calcium supplements are important for bone density and strength. Calcium deficiency in the elderly can lead to poor bone density, reduced mobility, and increased risk of falls.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D promotes bone strength and health when combined with calcium. The body naturally absorbs vitamin D from sunlight, but it is also found in fish like salmon,fortified milk and orange juice. Vitamin D deficiency is among the most common vitamin deficiencies as people age due to decreased mobility.
Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency is one of the most common micronutrient deficiencies.Foods rich in magnesium include whole grains, seeds, green leafy vegetables, and nuts. This mineral is essential for regulating glucose levels and blood pressure in the body.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for protein absorption and connective tissue creation for healing wounds. Citrus fruits, amla, tomatoes, and bell peppers contain Vitamin C.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E has antioxidant properties that boosts the immune system and prevent diseases caused by free radicals. Vitamin E is predominantly found in seeds, vegetable oils, and nuts.
Vitamin B6
B vitamins are required to support cognitive functioning and protein absorption. To improve Vitamin B levels, you can have potatoes, fish, sweet potatoes, and other starchy vegetables.
As we age, it is better to reduce the intake of oils, salts, etc., and eat more fruits and vegetables instead. As recommended by doctors, aging adults should consider taking specific food supplements to help vitamin intake.
Dietary supplements for the elderly
Elderly people may be unable to eat healthy, nutritious food for many reasons. However, help comes from dietary supplements to replenish the body with the missing nutrients.
Dietary supplements are not food, so you must be very cautious. Here’s what you should do before buying dietary supplements:
- Learn about dietary supplements as much as possible from a doctor, dietician, or pharmacist.
- Understand that all supplements may or may not work for you.
- Remember that many supplements are not natural, even if the product claims so. Some supplements can cause drastic side effects. If you are under medication, it could weaken or increase the medicine’s potential and make you prone to more harmful effects.
- Ask your doctor before deciding to start taking a dietary supplement to treat any health condition. Never take a supplement to diagnose or treat any health condition without your doctor’s consent.
- Buy brands that your doctor, dietitian, or pharmacist recommends. Also, buy only the recommended amount. Overdosing on supplements is very dangerous.
- Check for scientific proof. You must remember that most supplements listed have limited evidence of benefit.
- Be a savvy consumer and never fall for any of the claims made by the manufacturers. It is important to know that often, there is scarcely any scientific report to support these claims.
Is it safe to take dietary supplements?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) checks and regulates prescription medicines, like antibiotics, blood pressure drugs, and over-the-counter drugs for cough, cold, and pain, to ensure they are safe and do what they promise. Dietary supplements, however, are not regulated by the FDA; they do not need approval from the FDA for safety or efficacy before being sold.
Quality Supplements: How To Choose Them
Very often, the ingredients that go into supplements can interact with certain medications and adversely impact the senior person’s health. Therefore, it is imperative to seek professional guidance before using any supplement. You should also follow the directions to the T.
Be careful not to fall for attractive packaging and false statements. Make sure you buy only reputable brands that use high-quality ingredients. Also, avoid supplements containing additives, fillers, and artificial ingredients. Ensure the product has been tested for safety and quality by a third party.
Also Read This: Tips for Better Self-Care to Combat the Pandemic Fatigue
For more information or to partner with us on any REAN Foundation initiatives, please watch the entire video series here.
To learn more about REAN Foundation's unique healthcare platforms, download the REAN Health Guru App or visit https://www.reanfoundation.org/.
Intake of necessary nutrition is essential for individuals of all ages but it becomes critical as an individual reaches old age. Good nutrition crucially impacts all aspects of life, including physical, mental, and social health. As men and women age, their activity levels decrease, leading to a decrease in appetite. This low caloric intake often becomes one of the key factors in creating deficient levels of vitamins and minerals. The dietary deficiencies are also compounded by the presence of age-related chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis.
Why Do Seniors Lose Their Appetite?
Sudden loss of appetite and diminishing weight are not normal for anyone, irrespective of age. Why seniors experience such symptoms requires immediate medical evaluation to ascertain the reason. Loss of appetite can occur due to the following:
- Depression
- Stomach ulcers
- Cancers
- Dysphagia
- Thyroid issues
- Poor-fit dentures
- Failing sense of taste and smell
Work with your loved one's doctor instead of turning to a supplement immediately, and see if the underlying issues improve.
What are the main causes of nutrient deficiencies in seniors?
There are many causes that lead to dietary nutrient deficiency in older adults all over the world with degree of deficiencies varying from person to person. Some key causes of deficiencies are:
- Poor nutrient and dietary intake in the form of daily food consumption
- Physiological changes experienced by aging adults like forgetfulness, and loss of appetite
- Limiting financial conditions that impact quality food purchasing decisions
- Taking medications that hinder the body’s ability to absorb nutrients
As older adults are faced with physical, physiological and cognitive changes, poor dietary habits can result in the progression of chronic diseases like type II diabetes, atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and malnutrition. The lack of required nutrition in the body can lead to a decline in the general quality of life that relates to decreased physical function and cognitive decline. Other physical loss includes a decrease in bone density that increases the risk of osteoporosis. Loss of muscle mass, and malnutrition are issues related to older age which result in loss of strength, endurance and resistance to diseases.
Thus, the adoption of nutrient-rich foods can be a measure to tackle the situation of nutritional deficiencies and promote a healthy lifestyle.
The table below shares some common signs of nutritional deficiencies

Nutritional Deficiencies in Senior Adults
Aging brings on lesser physical activity and caloric intake. Nutrition deficiency becomes common as fewer essential minerals and vitamins get absorbed. The prevalence of nutritional deficiencies in seniors also occurs due to the following:
- Cognitive impairments like forgetfulness
- A reduced or limited income which limits the amount spent on food
- Side-effects of prolonged medication
- Interaction of certain medications with some vitamins and minerals
- Gastrointestinal issues and major surgical procedures.
- Smoking, tobacco usage, and over-consumption of alcohol.
- Neurotransmitter and hormonal changes.
How important are vitamins and minerals for maintaining good health?
As people enter their sixties and seventies, they are bound to feel weak due to nutritional deficiencies. Some of the most common deficiencies that seniors may have are:
Calcium
Leafy greens like kale and spinach, dairy products, and calcium supplements are important for bone density and strength. Calcium deficiency in the elderly can lead to poor bone density, reduced mobility, and increased risk of falls.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D promotes bone strength and health when combined with calcium. The body naturally absorbs vitamin D from sunlight, but it is also found in fish like salmon,fortified milk and orange juice. Vitamin D deficiency is among the most common vitamin deficiencies as people age due to decreased mobility.
Magnesium
Magnesium deficiency is one of the most common micronutrient deficiencies.Foods rich in magnesium include whole grains, seeds, green leafy vegetables, and nuts. This mineral is essential for regulating glucose levels and blood pressure in the body.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is essential for protein absorption and connective tissue creation for healing wounds. Citrus fruits, amla, tomatoes, and bell peppers contain Vitamin C.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E has antioxidant properties that boosts the immune system and prevent diseases caused by free radicals. Vitamin E is predominantly found in seeds, vegetable oils, and nuts.
Vitamin B6
B vitamins are required to support cognitive functioning and protein absorption. To improve Vitamin B levels, you can have potatoes, fish, sweet potatoes, and other starchy vegetables.
As we age, it is better to reduce the intake of oils, salts, etc., and eat more fruits and vegetables instead. As recommended by doctors, aging adults should consider taking specific food supplements to help vitamin intake.
Dietary supplements for the elderly
Elderly people may be unable to eat healthy, nutritious food for many reasons. However, help comes from dietary supplements to replenish the body with the missing nutrients.
Dietary supplements are not food, so you must be very cautious. Here’s what you should do before buying dietary supplements:
- Learn about dietary supplements as much as possible from a doctor, dietician, or pharmacist.
- Understand that all supplements may or may not work for you.
- Remember that many supplements are not natural, even if the product claims so. Some supplements can cause drastic side effects. If you are under medication, it could weaken or increase the medicine’s potential and make you prone to more harmful effects.
- Ask your doctor before deciding to start taking a dietary supplement to treat any health condition. Never take a supplement to diagnose or treat any health condition without your doctor’s consent.
- Buy brands that your doctor, dietitian, or pharmacist recommends. Also, buy only the recommended amount. Overdosing on supplements is very dangerous.
- Check for scientific proof. You must remember that most supplements listed have limited evidence of benefit.
- Be a savvy consumer and never fall for any of the claims made by the manufacturers. It is important to know that often, there is scarcely any scientific report to support these claims.
Is it safe to take dietary supplements?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) checks and regulates prescription medicines, like antibiotics, blood pressure drugs, and over-the-counter drugs for cough, cold, and pain, to ensure they are safe and do what they promise. Dietary supplements, however, are not regulated by the FDA; they do not need approval from the FDA for safety or efficacy before being sold.
Quality Supplements: How To Choose Them
Very often, the ingredients that go into supplements can interact with certain medications and adversely impact the senior person’s health. Therefore, it is imperative to seek professional guidance before using any supplement. You should also follow the directions to the T.
Be careful not to fall for attractive packaging and false statements. Make sure you buy only reputable brands that use high-quality ingredients. Also, avoid supplements containing additives, fillers, and artificial ingredients. Ensure the product has been tested for safety and quality by a third party.
Also Read This: Tips for Better Self-Care to Combat the Pandemic Fatigue
For more information or to partner with us on any REAN Foundation initiatives, please watch the entire video series here.
To learn more about REAN Foundation's unique healthcare platforms, download the REAN Health Guru App or visit https://www.reanfoundation.org/.



