Exploring How Stress Affects Your Body & Ways to Manage It
Stress is a natural physical and mental reaction to life's demands that you experience daily. Our bodies handle short-term stress effectively. However, chronic stress—that persistent tension keeping your muscles clenched and mind racing—damages physical health, mental clarity, and emotional stability over time.
This emotional cascade occurs because prolonged stress floods the systems meant for temporary crises, leaving your:
- Cardiovascular system strained
- Sleep patterns disrupted
- Immune defenses weakened
But how can you manage this stress effectively? Stress management strategies and digital platforms like REAN HealthGuru offer effective support in reducing and controlling stress.
This article breaks down the stress’s domino effect on the muscular, hormonal, and nervous systems, explaining acute triggers versus chronic health complications. Let’s discover how to recognize warning signs early and manage stress efficiently.
How Your Body Activates Its Internal Alarm System During Stress
When facing immediate threats, your body mounts an acute stress response—there are critical mechanisms in place designed to protect against danger. This defense system, known as the fight-or-flight response, prioritizes swift action by directing key changes across multiple biological systems.
Cortisol is released to redirect blood flow toward muscles and vital organs while suppressing less urgent functions such as digestion and reproductive processes. This hormone elevates blood sugar, providing ready energy for emergency action. Within moments, adrenaline accelerates the heart rate, increases blood pressure, sharpens awareness, and boosts the available energy supply for immediate physical demands.
This system works flawlessly during short-term stress to manage the immediate effects—you react swiftly and then return to calm. Prolonged stress, however, traps your body in survival mode. Chronic activation leads to persistently high levels of cortisol and adrenaline. Understanding these mechanics proves vital, as they set the stage for stress's downstream impacts on vulnerable systems like your cardiovascular network and respiratory pathways—areas we'll explore next.
Also Read: 10 Healthy Ideas To Handle Everyday Stress
The Impact of Stress on Your Cardiovascular & Respiratory Health
When stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol surge through your body, your cardiovascular system responds instantly. Your heart rate speeds up, and blood vessels constrict to redirect flow. This immediate reaction elevates your blood pressure as your heart pumps harder against narrowed vessels; hence, your system feels primed for action. Simultaneously, your respiratory system kicks in—you breathe faster, pulling more oxygen into your lungs to fuel muscles for potential fight or flight.
While effective in the short term, chronic stress keeps this system on high alert. Imagine the relentless strain on your heart and arteries working overtime constantly. Therefore, your long-term risk for serious health issues increases. This includes:
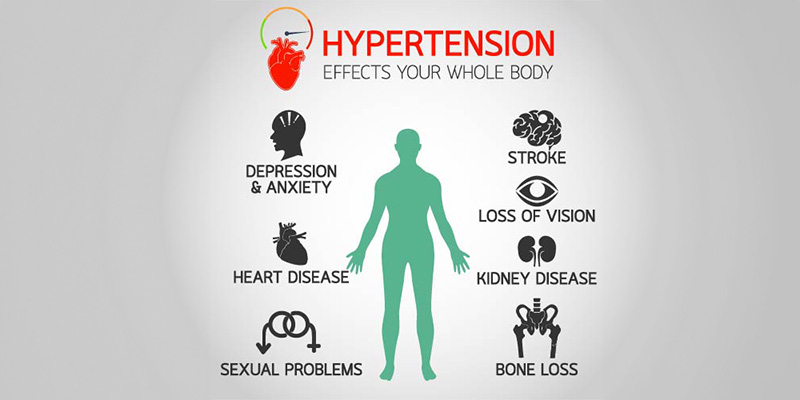
- Hypertension: Persistently elevated blood pressure damages vessel walls.
- Heart attack: Ongoing strain and potential blockages raise this risk.
- Stroke: Weakened blood vessels become more vulnerable.
Furthermore, for those with conditions like asthma, the faster “stress breathing” can easily trigger episodes of severe shortness of breath, making simple activities feel exhausting. These cardiovascular and respiratory problems clearly show the damaging effects of stress on the body. Yet, the impact doesn't stop here.
Next, we'll explore how prolonged tension disrupts your digestive health and muscular systems.
How Stress Disrupts Your Digestive & Muscular Systems
When stress hormones flood your system during extended challenging periods, they can throw your digestive health out of balance. One key player—cortisol—signals your liver to release extra glucose for immediate energy demands. However, frequent activation of this process can overwhelm your body and potentially contribute to issues like insulin resistance over time.
Your entire digestive process may suffer under prolonged stress. There are several ways this can manifest:
- Nutrient absorption slows down as blood flow is redirected away from the digestive muscles.
- Stomach acid production can increase, potentially causing heartburn and reflux.
- Intestinal contraction speeds become irregular, resulting in either diarrhea or constipation.
- Gut–brain communication disruption may trigger nausea or abdominal cramps.
Meanwhile, stress triggers primal defense responses that directly impact your musculoskeletal health. Your muscles tense up reflexively. Under chronic stress, this muscle tension doesn't release, creating persistent tightness often felt across the shoulders, neck, and back.
The next section discusses how stress impacts the immune function of your body and reproductive health.
Effects of Stress on the Body’s Immune Function & Reproductive Health
Short-term stress can trigger a temporary boost in immune alertness due to cortisol release. However, prolonged or chronic stress has the opposite effect, weakening your body’s ability to fight off infections. Persistent stress can lead to chronic inflammation and suppress overall immune function, leaving you more vulnerable to illnesses.
Beyond immunity, the hormonal disruption caused by chronic stress significantly impacts the reproductive system in both sexes. Cortisol overload can interfere with the production and balance of crucial sex hormones.
- In women, chronic stress can disrupt normal menstrual cycles, potentially leading to irregularities or changes in flow, and may negatively impact fertility.
- In men, stress can affect testosterone production and sperm health, potentially leading to decreased libido or challenges with fertility.
These hormonal imbalances highlight how deeply stress can affect fundamental bodily processes. Left unchecked, chronic stress can contribute to various reproductive health concerns over time.
In the next section, we'll unfurl the common physical, emotional, and behavioral signs of stress.
Recognizing Common Physical, Emotional, & Behavioral Signs of Stress
When stress persists, your body sends clear warning signs. Recognizing these common signals is key to managing the effects of stress on the body.
Physical Signs
- Headaches, muscle tension, and tightness from a sustained fight-or-flight response.
- Fatigue and sleep issues due to hormonal imbalances.
- Chest pain and rapid heartbeat—adrenaline surges impacting heart function.
- Slowed digestion, causing stomach upset or reflux.
- Frequent colds due to a weakened immune system caused by chronic cortisol.
Emotional Signs
- Anxiety and restlessness caused by an overactive stress response (HPA axis).
- Focus and memory issues occur when cortisol affects brain function, leading to brain fog.
- Irritability, anger, and lowered tolerance from feeling constantly overwhelmed.
- Sadness or low mood because emotional reserves are depleted by ongoing stress.
Behavioral Signs
- Appetite changes due to cortisol impacting hunger cues (over-/under-eating).
- Social withdrawal or feeling too exhausted to connect with others.
- Increased usage of alcohol/drugs to cope.
- Difficulty engaging in daily tasks or hobbies.
Identifying these patterns empowers early action. Next, let's explore effective coping strategies.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stress to Improve Your Quality of Life
Recognizing the signs of stress is the first step, but actively managing it is crucial for protecting your physical and mental well-being. Here are six practical strategies you can implement:
1. Know Your Stress Triggers
Identify what situations, thoughts, or events trigger your stress levels. Knowing your own triggers allows you to expect challenges and respond better to them.
2. Adhere to Healthy Habits/Routines
Make regular physical activity a priority, achieve consistent and sufficient sleep, and fuel your body with a healthy, balanced diet. These core habits enhance your stress resistance.
3. Emphasize Relaxation Techniques
Voluntarily/intentionally plan activities that soothe your body and mind. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or even listening to music or reading can reverse day-to-day stress.
4. Develop Organizational Skills
If tasks or workload seem overwhelming, divide big tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Lists, calendars, or apps can assist you in feeling more in charge/in control.
5. Reach Out to Your Support Network
Don't be afraid to reach out to trusted friends, family, or support groups. Exchanging experiences and receiving encouragement greatly diminishes loneliness/feelings of isolation and fosters emotional strength.
6. Take the Step to Get Professional Support
When stress becomes persistent or unmanageable, seek a therapist or counselor. They offer professional advice to find underlying causes and create individualized, effective coping mechanisms.
Implementing these strategies can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on your body and improve your overall quality of life.
Take Proactive Steps to Reduce Stress & Enhance Your Well-Being
Your entire physiology pays the price when stress becomes chronic, disrupting crucial systems and triggering severe physical and emotional disorders. Recognizing early signs like anxiety or digestive issues allows you to intercept this cascade before permanent damage occurs.
If you're experiencing chest pain or suicidal thoughts that basic strategies can't resolve, counselors and medical professionals offer essential lifelines. They help untangle stress's complex web through techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy that address hormonal imbalances and muscular tension simultaneously.
At REAN Foundation, we empower people globally to manage stress proactively using our personalized digital health tools. Our app combines modern monitoring with expert-backed strategies to help you take charge of your well-being—one step at a time.
Ready to start your journey to better health? Connect with us today and regain command of your physical and mental well-being!
Stress is a natural physical and mental reaction to life's demands that you experience daily. Our bodies handle short-term stress effectively. However, chronic stress—that persistent tension keeping your muscles clenched and mind racing—damages physical health, mental clarity, and emotional stability over time.
This emotional cascade occurs because prolonged stress floods the systems meant for temporary crises, leaving your:
- Cardiovascular system strained
- Sleep patterns disrupted
- Immune defenses weakened
But how can you manage this stress effectively? Stress management strategies and digital platforms like REAN HealthGuru offer effective support in reducing and controlling stress.
This article breaks down the stress’s domino effect on the muscular, hormonal, and nervous systems, explaining acute triggers versus chronic health complications. Let’s discover how to recognize warning signs early and manage stress efficiently.
How Your Body Activates Its Internal Alarm System During Stress
When facing immediate threats, your body mounts an acute stress response—there are critical mechanisms in place designed to protect against danger. This defense system, known as the fight-or-flight response, prioritizes swift action by directing key changes across multiple biological systems.
Cortisol is released to redirect blood flow toward muscles and vital organs while suppressing less urgent functions such as digestion and reproductive processes. This hormone elevates blood sugar, providing ready energy for emergency action. Within moments, adrenaline accelerates the heart rate, increases blood pressure, sharpens awareness, and boosts the available energy supply for immediate physical demands.
This system works flawlessly during short-term stress to manage the immediate effects—you react swiftly and then return to calm. Prolonged stress, however, traps your body in survival mode. Chronic activation leads to persistently high levels of cortisol and adrenaline. Understanding these mechanics proves vital, as they set the stage for stress's downstream impacts on vulnerable systems like your cardiovascular network and respiratory pathways—areas we'll explore next.
Also Read: 10 Healthy Ideas To Handle Everyday Stress
The Impact of Stress on Your Cardiovascular & Respiratory Health
When stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol surge through your body, your cardiovascular system responds instantly. Your heart rate speeds up, and blood vessels constrict to redirect flow. This immediate reaction elevates your blood pressure as your heart pumps harder against narrowed vessels; hence, your system feels primed for action. Simultaneously, your respiratory system kicks in—you breathe faster, pulling more oxygen into your lungs to fuel muscles for potential fight or flight.
While effective in the short term, chronic stress keeps this system on high alert. Imagine the relentless strain on your heart and arteries working overtime constantly. Therefore, your long-term risk for serious health issues increases. This includes:
- Hypertension: Persistently elevated blood pressure damages vessel walls.
- Heart attack: Ongoing strain and potential blockages raise this risk.
- Stroke: Weakened blood vessels become more vulnerable.
Furthermore, for those with conditions like asthma, the faster “stress breathing” can easily trigger episodes of severe shortness of breath, making simple activities feel exhausting. These cardiovascular and respiratory problems clearly show the damaging effects of stress on the body. Yet, the impact doesn't stop here.
Next, we'll explore how prolonged tension disrupts your digestive health and muscular systems.
How Stress Disrupts Your Digestive & Muscular Systems
When stress hormones flood your system during extended challenging periods, they can throw your digestive health out of balance. One key player—cortisol—signals your liver to release extra glucose for immediate energy demands. However, frequent activation of this process can overwhelm your body and potentially contribute to issues like insulin resistance over time.
Your entire digestive process may suffer under prolonged stress. There are several ways this can manifest:
- Nutrient absorption slows down as blood flow is redirected away from the digestive muscles.
- Stomach acid production can increase, potentially causing heartburn and reflux.
- Intestinal contraction speeds become irregular, resulting in either diarrhea or constipation.
- Gut–brain communication disruption may trigger nausea or abdominal cramps.
Meanwhile, stress triggers primal defense responses that directly impact your musculoskeletal health. Your muscles tense up reflexively. Under chronic stress, this muscle tension doesn't release, creating persistent tightness often felt across the shoulders, neck, and back.
The next section discusses how stress impacts the immune function of your body and reproductive health.
Effects of Stress on the Body’s Immune Function & Reproductive Health
Short-term stress can trigger a temporary boost in immune alertness due to cortisol release. However, prolonged or chronic stress has the opposite effect, weakening your body’s ability to fight off infections. Persistent stress can lead to chronic inflammation and suppress overall immune function, leaving you more vulnerable to illnesses.
Beyond immunity, the hormonal disruption caused by chronic stress significantly impacts the reproductive system in both sexes. Cortisol overload can interfere with the production and balance of crucial sex hormones.
- In women, chronic stress can disrupt normal menstrual cycles, potentially leading to irregularities or changes in flow, and may negatively impact fertility.
- In men, stress can affect testosterone production and sperm health, potentially leading to decreased libido or challenges with fertility.
These hormonal imbalances highlight how deeply stress can affect fundamental bodily processes. Left unchecked, chronic stress can contribute to various reproductive health concerns over time.
In the next section, we'll unfurl the common physical, emotional, and behavioral signs of stress.
Recognizing Common Physical, Emotional, & Behavioral Signs of Stress
When stress persists, your body sends clear warning signs. Recognizing these common signals is key to managing the effects of stress on the body.
Physical Signs
- Headaches, muscle tension, and tightness from a sustained fight-or-flight response.
- Fatigue and sleep issues due to hormonal imbalances.
- Chest pain and rapid heartbeat—adrenaline surges impacting heart function.
- Slowed digestion, causing stomach upset or reflux.
- Frequent colds due to a weakened immune system caused by chronic cortisol.
Emotional Signs
- Anxiety and restlessness caused by an overactive stress response (HPA axis).
- Focus and memory issues occur when cortisol affects brain function, leading to brain fog.
- Irritability, anger, and lowered tolerance from feeling constantly overwhelmed.
- Sadness or low mood because emotional reserves are depleted by ongoing stress.
Behavioral Signs
- Appetite changes due to cortisol impacting hunger cues (over-/under-eating).
- Social withdrawal or feeling too exhausted to connect with others.
- Increased usage of alcohol/drugs to cope.
- Difficulty engaging in daily tasks or hobbies.
Identifying these patterns empowers early action. Next, let's explore effective coping strategies.
Effective Strategies for Managing Stress to Improve Your Quality of Life
Recognizing the signs of stress is the first step, but actively managing it is crucial for protecting your physical and mental well-being. Here are six practical strategies you can implement:
1. Know Your Stress Triggers
Identify what situations, thoughts, or events trigger your stress levels. Knowing your own triggers allows you to expect challenges and respond better to them.
2. Adhere to Healthy Habits/Routines
Make regular physical activity a priority, achieve consistent and sufficient sleep, and fuel your body with a healthy, balanced diet. These core habits enhance your stress resistance.
3. Emphasize Relaxation Techniques
Voluntarily/intentionally plan activities that soothe your body and mind. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or even listening to music or reading can reverse day-to-day stress.
4. Develop Organizational Skills
If tasks or workload seem overwhelming, divide big tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Lists, calendars, or apps can assist you in feeling more in charge/in control.
5. Reach Out to Your Support Network
Don't be afraid to reach out to trusted friends, family, or support groups. Exchanging experiences and receiving encouragement greatly diminishes loneliness/feelings of isolation and fosters emotional strength.
6. Take the Step to Get Professional Support
When stress becomes persistent or unmanageable, seek a therapist or counselor. They offer professional advice to find underlying causes and create individualized, effective coping mechanisms.
Implementing these strategies can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on your body and improve your overall quality of life.
Take Proactive Steps to Reduce Stress & Enhance Your Well-Being
Your entire physiology pays the price when stress becomes chronic, disrupting crucial systems and triggering severe physical and emotional disorders. Recognizing early signs like anxiety or digestive issues allows you to intercept this cascade before permanent damage occurs.
If you're experiencing chest pain or suicidal thoughts that basic strategies can't resolve, counselors and medical professionals offer essential lifelines. They help untangle stress's complex web through techniques like cognitive behavioral therapy that address hormonal imbalances and muscular tension simultaneously.
At REAN Foundation, we empower people globally to manage stress proactively using our personalized digital health tools. Our app combines modern monitoring with expert-backed strategies to help you take charge of your well-being—one step at a time.
Ready to start your journey to better health? Connect with us today and regain command of your physical and mental well-being!



